
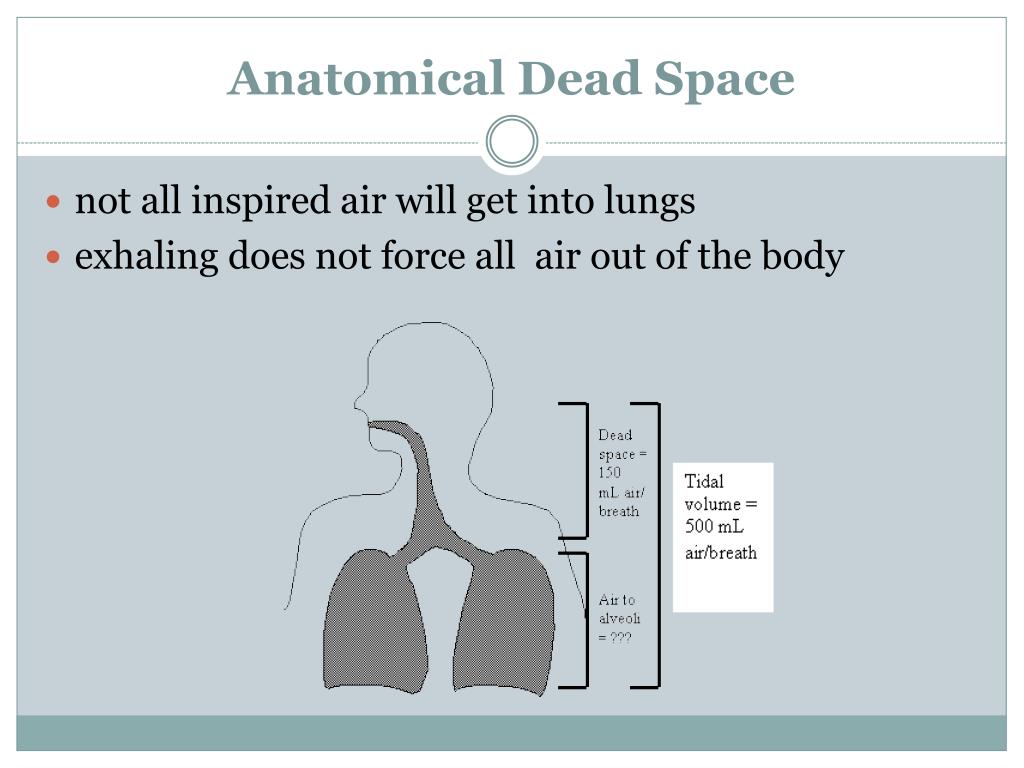
(V co2) = (V aFaco2)-(V iFico2), where Vco2 is the difference between the CO2 expired from the alveoli and the amount of CO2 inspired to the alveoli. The Fick equation (see Chapter 18) defines CO2 elimination from the lungs (Vco2) as: 10) but gas exchange principles can be used to obtain a more direct measure of the effective, or functional, alveolar ventilation.Īlveolar Ventilation Equation Predicts Paco2 Anatomic dead space can be measured with the single breath method (see Chapter 18, Fig.

Va = /R(Vt - Vd), where Va is alveolar ventilation, fR is respiratory frequency, Vt is tidal volume, and Vd is anatomic dead space. As described in Chapter 18, anatomic dead space reduces the fraction of the tidal volume that reaches the alveoli: Ventilation is the first step in the O2 cascade, and the level of alveolar ventilation (Va) is the most important physiologic factor determining arterial Po2 for any given inspired Po2 and level of O2 demand (Vo2) in healthy lungs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
